Transform your home into a self-sustaining energy hub with off-grid solar systems in Vancouver and beyond. Modern solar technology now enables complete energy independence, offering freedom from utility bills while protecting against power outages and reducing environmental impact.
Start your off-grid solar journey by conducting a comprehensive energy audit to determine your daily power requirements. Calculate everything from basic lighting and appliances to seasonal heating and cooling demands. Next, assess your property’s solar potential by measuring available roof space, sun exposure hours, and shading patterns throughout the year. Factor in British Columbia’s unique climate patterns, including our cloudy winter months and long summer days, to design a system that performs year-round.
Your off-grid solar setup requires careful planning and strategic component selection. Beyond solar panels, you’ll need robust battery storage, charge controllers, and inverters sized specifically for your needs. Consider starting with a smaller system that can expand as your energy needs grow, allowing for a more manageable initial investment while gaining valuable experience in off-grid living.
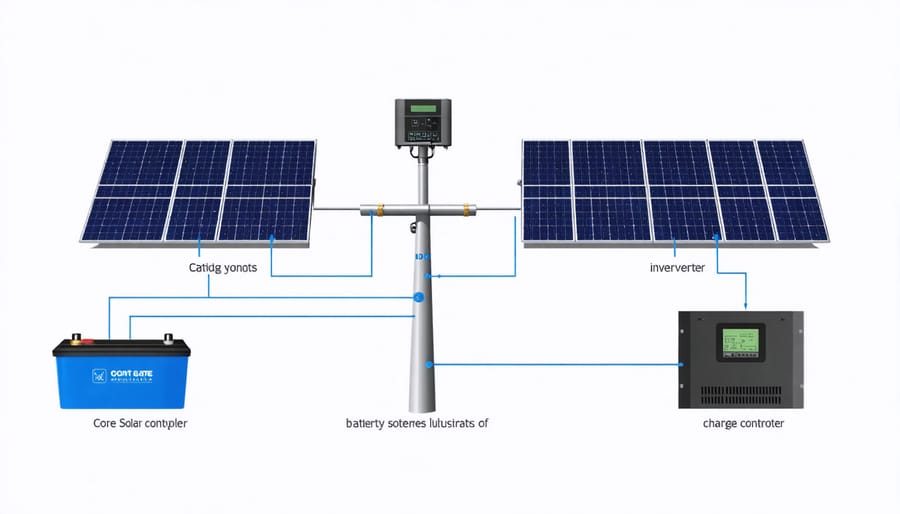
Essential Components of an Off-Grid Solar System
Solar Panels and Array Design
For the BC climate, monocrystalline solar panels offer the best performance due to their superior efficiency in low-light conditions and cooler temperatures. These panels typically convert 15-22% of sunlight into electricity, making them ideal for our shorter winter days and frequent cloud cover.
When designing your array, south-facing installation at a 30-45 degree angle provides optimal year-round energy collection in most BC locations. However, east-west configurations can also work well, especially if you’re aiming to capture both morning and afternoon sun. For snow-heavy regions like the Interior, consider a steeper angle (up to 60 degrees) to promote natural snow shedding.
The size of your array depends on your energy needs, but most off-grid homes in BC require between 4-8 kW systems. Using higher-wattage panels (400W+) means you’ll need fewer panels overall, reducing installation complexity and roof space requirements. For maximum durability, look for panels rated for high snow loads (5400 Pa) and with robust weather sealing to handle our wet coastal climate.
Remember to leave room for system expansion – many off-grid homeowners find their energy needs grow over time as they add more appliances or electric vehicles to their setup.
Battery Storage Solutions
Battery storage is the backbone of any off-grid solar system, especially in British Columbia where winter months bring shorter days and less sunlight. For year-round power reliability, choosing the right battery technology and size is crucial.
Lithium-ion batteries have become the go-to choice for many BC homeowners due to their longer lifespan, better depth of discharge, and compact size. While the upfront cost is higher than traditional lead-acid batteries, they typically last 10-15 years and require minimal maintenance. For a typical off-grid home in BC, a 10-20 kWh lithium battery bank often provides sufficient storage for daily use.
Lead-acid batteries remain a budget-friendly option, with many local success stories of homeowners using them effectively. These batteries require more maintenance and have a shorter lifespan (5-10 years), but their lower initial cost makes them attractive for those starting their off-grid journey.
To properly size your battery bank, consider your daily power consumption and add a 20% buffer for unexpected needs. Most BC off-grid homes need enough storage to power through 3-4 days of cloudy weather. For example, a household using 15 kWh daily should aim for a 45-60 kWh battery bank.
Remember to factor in temperature control for your battery storage area, as BC’s climate can affect battery performance. A well-insulated, climate-controlled space helps maximize battery life and efficiency.

Inverters and Charge Controllers
Inverters and charge controllers are the brains of your off-grid solar system, working together to manage power flow and protect your batteries. For BC’s varying seasonal conditions, we recommend MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) charge controllers, which can increase system efficiency by up to 30% compared to standard controllers. They’re particularly effective during our cloudy winter months.
When selecting an inverter, consider whether you need a pure sine wave or modified sine wave model. Pure sine wave inverters, though more expensive, are essential for sensitive electronics and medical equipment. For most off-grid homes in BC, we suggest a pure sine wave inverter rated at least 20% above your expected peak load.
Look for inverters with built-in battery monitoring and cold-weather performance ratings. Many local off-gridders have found success with hybrid inverter-chargers, which can automatically switch between solar and backup power sources. Remember to size your equipment based on both your current needs and potential future expansion – it’s more cost-effective to slightly oversize now than to upgrade later.
Planning Your System for BC’s Climate
Calculating Your Power Needs
Determining your power needs is the crucial first step in designing your off-grid solar system. In British Columbia, average household electricity consumption varies significantly based on home size, heating methods, and lifestyle choices. To calculate your requirements, start by listing all your electrical appliances and their wattage ratings.
Create a detailed energy audit by monitoring your current usage through utility bills or a power meter. Pay special attention to power-hungry appliances like electric heating, water heaters, and kitchen equipment. Remember to account for seasonal variations – BC winters mean shorter days and increased heating needs, while summer brings longer daylight hours but potential air conditioning usage.
Consider your daily routines and peak usage times. For example, if you work from home, your daytime energy needs might be higher. Factor in a 20% buffer for unexpected needs and system inefficiencies. Many BC residents find their winter consumption can be double their summer usage, so plan accordingly.
To simplify this process, maintain a power diary for a week in each season. Record when you use major appliances and for how long. This real-world data will help you design a system that truly meets your needs rather than relying on general estimates. Remember, efficient energy use habits can significantly reduce your required system size and cost.
Weather Patterns and Solar Potential
British Columbia’s diverse climate zones present unique considerations for off-grid solar power systems. While coastal regions experience frequent cloud cover and rain, interior areas enjoy more sunny days, significantly impacting solar panel performance in cloudy conditions. Understanding your local weather patterns is crucial for designing an efficient off-grid system.
The good news is that modern solar technology works effectively even in BC’s varied climate. Vancouver Island and the Lower Mainland receive approximately 2,000 hours of sunshine annually, while the Okanagan Valley benefits from over 2,200 hours. Even during overcast days, panels typically generate 10-25% of their rated capacity.
To maximize your solar potential:
– Track your location’s solar hours using local weather data
– Consider seasonal variations in sunlight availability
– Plan for additional battery storage during winter months
– Install panels at optimal angles for your latitude
– Account for snow load in mountain regions
– Monitor weather forecasts for system management
Many successful off-grid homeowners in BC combine solar with other renewable sources, creating hybrid systems that ensure reliable power year-round. Weather monitoring tools and solar calculators can help you assess your specific location’s potential and design a system that meets your needs throughout the seasons.
Backup Power Solutions
While solar power is highly reliable, having backup power solutions is essential for off-grid living in British Columbia, especially during the darker winter months or extended periods of cloudy weather. A hybrid approach combining different power sources ensures continuous electricity supply for your home.
Generator backup systems are the most common solution, with propane generators being particularly popular due to their clean-burning properties and the fuel’s long shelf life. Many BC residents opt for automatic transfer switches that seamlessly transition to generator power when solar battery levels drop below a certain threshold.
Alternative backup solutions include micro-hydro systems for properties with running water sources, and small wind turbines that can complement solar production, particularly during winter when solar generation is lower but wind speeds are typically higher. Some homeowners in BC’s interior regions have successfully integrated micro-hydro systems that provide consistent power output year-round.
Battery capacity is crucial for any backup system. Modern lithium-ion batteries offer excellent performance and longevity, though some residents still prefer traditional lead-acid batteries for their lower initial cost. When designing your backup system, consider sizing it to support essential loads for at least 3-5 days of autonomy, accounting for BC’s seasonal weather patterns.
Remember to regularly maintain your backup systems and store fuel safely according to local regulations. Many off-grid communities in BC have established equipment-sharing programs, making backup power solutions more accessible and cost-effective for everyone.
Installation and Maintenance
Professional vs. DIY Installation
When it comes to setting up your off-grid solar system in British Columbia, you’ll need to decide between professional installation and DIY solar installation. Each option has its own set of advantages and considerations.
Professional installation offers peace of mind through expertise and warranty coverage. Certified installers understand local building codes, electrical requirements, and permitting processes specific to BC municipalities. They can properly assess your roof’s structural integrity, optimize panel placement for maximum efficiency, and ensure all electrical connections meet safety standards. Many insurance companies also prefer professionally installed systems.
However, the DIY route can significantly reduce upfront costs, typically saving 10-30% on installation expenses. This option works well for those with electrical experience and a solid understanding of solar systems. Keep in mind that in BC, you’ll still need to obtain proper permits and have your work inspected by a certified electrician.
Local regulations vary by municipality, but generally require:
– Building permits
– Electrical permits
– Professional inspection
– Grid connection approval (if maintaining a grid backup)
Many successful off-grid residents in BC have found middle-ground solutions, such as hiring professionals for critical components while handling simpler tasks themselves. Some suppliers offer hybrid services, providing technical support and guidance while you complete the installation.
Before making your decision, consider your technical skills, available time, local regulations, and insurance requirements. Remember that proper installation is crucial for system performance and longevity, regardless of which path you choose.
System Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance of your off-grid solar system is essential for optimal performance and longevity. In BC’s diverse climate, we recommend checking your system components at least once every three months, with more frequent inspections during winter months when snow accumulation can affect panel efficiency.
Start with a visual inspection of your solar panels. Look for dust, pine needles, or snow buildup, and gently clean the panels using warm water and a soft brush. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage the panel surface. During winter, invest in a proper snow rake designed specifically for solar panels to prevent damage while clearing snow.
Monitor your battery bank’s performance by checking voltage levels regularly and maintaining proper electrolyte levels in flooded lead-acid batteries. Keep a logbook to track battery readings, helping you identify potential issues before they become serious problems. In BC’s colder regions, ensure your batteries are stored in an insulated space where temperatures remain above freezing.
Check all electrical connections monthly for signs of corrosion or loose wiring, especially in coastal areas where salt air can accelerate deterioration. Inspect your charge controller’s display for any error messages or unusual readings, and verify that your inverter is functioning correctly by listening for unusual sounds or checking its LED indicators.
Many BC residents find it helpful to schedule professional maintenance at least once a year. Local solar experts can perform detailed system diagnostics, test equipment efficiency, and recommend upgrades or replacements before components fail. Remember, preventive maintenance is always more cost-effective than emergency repairs, especially in remote locations where service calls can be expensive.
Cost Considerations and Incentives
Initial Investment and Long-term Savings
Making the switch to solar power requires careful financial planning, but the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial costs. In British Columbia, a typical off-grid solar system for a modest home ranges from $30,000 to $45,000, including panels, batteries, inverters, and installation. This investment varies based on your energy needs, location, and system size.
For example, a 3-bedroom home in the Interior region might require a 10kW system with battery storage, costing approximately $35,000. While this might seem substantial, provincial rebates and federal incentives can reduce these costs by 20-30%. The CleanBC program offers up to $5,000 in rebates for qualifying installations, making the transition more affordable.
The return on investment typically occurs within 8-12 years, depending on your current energy costs and usage patterns. Many BC homeowners report monthly savings of $150-250 on electricity bills, translating to annual savings of $1,800-3,000. Additionally, modern solar equipment comes with extended warranties – panels often lasting 25-30 years – providing decades of reliable power generation.
Beyond direct financial returns, off-grid solar systems increase property values by an average of 4%. They also offer independence from rising utility costs and protection against power outages, which is particularly valuable in remote BC locations. When properly maintained, your solar investment can provide reliable power for decades while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Available Rebates and Programs
British Columbia offers several valuable incentives for residents transitioning to off-grid solar power systems. The CleanBC Better Homes program provides significant rebates for homeowners installing renewable energy systems, including solar energy grants in BC that can cover up to $5,000 of your installation costs.
Indigenous communities can access additional funding through the Indigenous Clean Energy Initiative, which supports sustainable energy projects in remote areas. The Canada Greener Homes Grant adds another layer of support, offering up to $5,000 for energy-efficient home improvements, including solar installations.
Local municipalities often provide supplementary incentives. For example, Nelson’s EcoSave program offers low-interest financing options for renewable energy projects, while Vancouver’s Zero Emissions Building Plan includes provisions for solar installations.
Rural property owners can benefit from BC Hydro’s Net Metering program, even when primarily off-grid. This allows you to connect to the grid occasionally and receive credits for any excess power you generate.
For businesses and farms, the Canadian Agricultural Clean Technology Program provides funding specifically for agricultural operations transitioning to renewable energy sources. Remember to check with your local solar installer, as they often have up-to-date information about seasonal promotions and additional manufacturer rebates.
Embarking on your off-grid solar journey in British Columbia opens up a world of energy independence and sustainable living. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential components of solar power systems, from panels and batteries to inverters and charge controllers. We’ve also discussed the importance of proper sizing, local climate considerations, and the specific regulations that apply to BC residents.
Remember that successful off-grid living requires careful planning and a thorough understanding of your energy needs. Start by conducting a detailed energy audit of your intended lifestyle, then work with local solar professionals to design a system that meets those needs while accounting for BC’s unique seasonal variations in sunlight.
Your next steps should include:
– Calculating your daily energy requirements
– Consulting with certified solar installers in your region
– Reviewing local building codes and permit requirements
– Creating a realistic budget that includes maintenance costs
– Developing an energy management strategy for year-round operation
The transition to off-grid solar living is both challenging and rewarding. While the initial investment may seem substantial, the long-term benefits of energy independence, reduced environmental impact, and sustainable living make it worthwhile. Join the growing community of off-grid enthusiasts in BC who are leading the way toward a more sustainable future.
For personalized guidance and support, reach out to local solar providers and connect with experienced off-grid residents who can share their valuable insights and lessons learned.

